Types of Art: Explanation of Major Art Forms (with Examples)

What is art, and how can it be classified? With so many different types of art available, it can be hard to choose which would be a best fit for you, especially as a beginner.
It you understand how to classify art, it will help you to understand where your strengths and interests can make the biggest impact.
The task of categorizing art, however, is difficult, and no single method is sufficient. This is mainly because:
- There is an overwhelming number of art styles and forms.
- People classify art in different ways, and there is no universal agreement.
In this article, I will give a general overview of art and how it is classified. In particular, I will:
- Give a simple definition of art.
- Explain how art has traditionally been classified (i.e. the seven traditional art forms).
- Examine the shortcomings of traditional methods of classifying art, and explore other ways to classify art.
- Explain the various types of art in detail.
By the end of the article, you should be able to understand where any art you encounter fits.
This will make it easier to find the perfect art niche for your particular strengths and mode of creative expression.
This is important if you want to get into art, either as a hobby or a career.
Let us dive in.
1. What is Art?
To classify art adequately, you should define it clearly and understand its characteristics.
So, what is art?
Art can be defined as creative works of beauty or emotional appeal which express the creator’s feelings and vision. Art is created through the application of skill and imagination. [1]
Any definition of art is likely to be insufficient because it is incredibly broad and encompasses many aspects.
When defining art, it helps to look at the various aspects of art. Art:
- Involves the creation of aesthetic works. We enjoy beautiful art through our five senses.
- Helps to communicate or share the artists’ ideas, emotions, experiences, and beliefs. Art is a form of catharsis where the artist feels compelled to release what is inside.
- Involves the application of creativity, imagination, and skill to create original work.
- Art arouses feelings and emotions in us. Good art will make you feel something.
- Depicts nature in all its forms (living and non-living)
Art comes in various forms (such as audial, visual, and kinetic). Here are examples of art forms.
- Music that communicates the emotions, lessons, or beliefs of the musician.
- Religious art that conveys the beliefs, stories, or experiences of the believers.
- Sculptures of religious, political, or other prominent figures of society.
- A play that depicts a battle in history or promotes certain cultural values.
Unlock Your Creative Mastery
DOMESTIKA
You now have a way to attain mastery in your creative hobbies without breaking the bank.
With Domestika Plus, you get access to over 1,000 high-quality courses for only $7.83 a month (or $93.99 a year). You also get:
2. Traditional Forms of Art (The 7 Forms of Art)
Traditionally, art has been categorized into seven forms. [2] These seven forms give us a broad method of classifying art, but as we will see, they have their limitations.
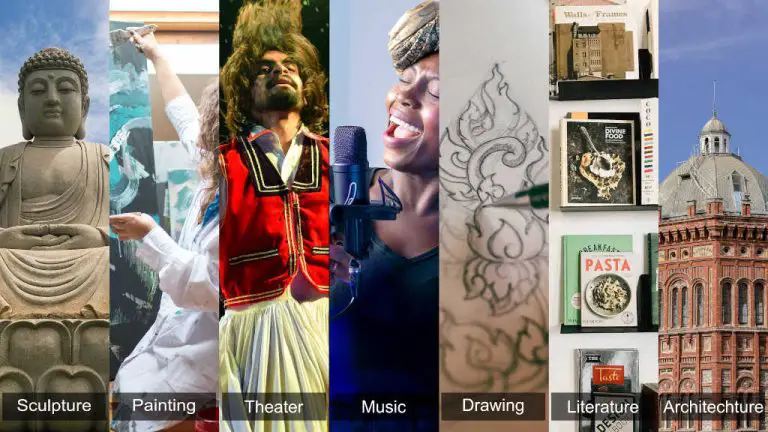

The 7 forms of art are:
- Painting. This is a form of art that uses paint as the primary medium.
- Sculpture. Sculptures are three-dimensional works of art, such as carvings, and statues.
- Literature. This isart through written works.
- Architecture. This is the art of designing and constructing buildings.
- Cinema. This is art through moving images that tell stories.
- Music. This is an audio form of art where instruments or human voices are used to express emotions or pass ideas.
- Theater. This is a form of art that uses live performances.
3. Limitations of the Traditional Method of Categorizing Art
The traditional way of classifying art (into the 7 forms) has worked well, but as art evolves, it becomes difficult to fit into the newer art forms.
For example, where would you place art forms such as graphic design, animations, digital art, and web design?
You either have to modify the definitions of the seven art forms or come up with new classes.
Having said that, no method of classifying art will be perfect.
The task of categorizing art into types is hard because:
- Art is broad, and there is an overwhelming number of art styles and forms.
- Art is always evolving, and it can be difficult to categorize emerging forms of art adequately.
- Definitions of the different art forms can be hazy. This means that different arts can appear in more than one category.
- Different people classify art in different ways and there is no consensus on any particular method. Given that classifying art is inherently subjective, this can lead to endless arguments.
- Some artists don’t like being put in a box and detest the idea of classifying art.
- Some people feel that categorizing art leads to hierarchies. For example, someone in fine art may consider someone in applied art as an inferior artist (see Arts versus Crafts).
Nonetheless, classifying art makes it easy for an ordinary person to make sense of the countless existing art forms.
So, for the rest of this article, I will explore other ways of classifying art and explain the different examples of art that fall under them.
4. How Do You Classify Art? The Main Methods of Classifying Art
Because of the limitations of the traditional way of classifying art, people have come up with other ways to classify art that may better suit their purposes.
Some of the common factors people use to classify art include:
- The intent of the art.
- The form of the art.
- The materials used.
- Where the art originated.
- The period or era when the art was produced.
- The function of the art.
Let us look at them in detail.
#1. The intent of the art
Artists create art with two major motivations:
- For self-expression. Here the artist creates works of aesthetic or emotional appeal.
- To produce practical objects. Here, art is used to beautify everyday objects like clothes, mats, and bowls (often for sale).
Based on these major motivations, you can classify art into two types.
- Fine (Pure) art: This is art created for its own sake (often aesthetic or emotional satisfaction). These include paintings, drawings, and sculptures. Fine art can be further divided into 3 types: visual, performing, and literary arts.
- Applied art: This is art created for a practical function. Applied art can be divided into two types: decoration arts and design arts.
#2. The form of art
Art can be categorized based on form. By form, I mean how art is expressed or perceived.
Here are common types of art based on form.
- Visual Art. This is art that is primarily enjoyed through the sense of sight. It encompasses many categories of art including 2D Art (paintings, drawings, and photographs), 3D Art (carvings, reliefs, and models), video art (film, animations, and music videos), and decorative arts (etching, staining, and embroidery).
- Audio Art: This is art that is primarily meant to be heard, for example, music, spoken word, beats, and radio.
- Performing Art. This is art that is performed live, for example, theater, DJing, live music performance, miming, and spoken word.
- Literary Art. This is art in written form, for example, fiction and non-fiction writing.
#3. The Materials Used
Materials like wood, clay, metal, or stone are used in various kinds of art. You can group art based on the type of material used.
The common types of art based on materials used are:
- Wood Arts. These include wood carving, engraving, woodcuts, and wood burning (pyrography).
- Clay Arts. These include modeling, ceramics, casting, and sgraffito.
- Metal Arts. These include etching, casting, gilding, enameling, and stamping.
- Stone Arts. These include carving, engraving, polishing, flaming, and sandblasting.
- Glass Arts. These include staining, enameling, millefiori, etching, and engraving.
#4. Location
You can also classify art based on where it was produced originally or where it is most common.
Artworks produced in a particular place tend to have similar characteristics that differentiate them from art made elsewhere.
Below are examples of how you can categorize art based on location.
- African Art. This is art from sub-Saharan Africa. It is characterized by masks and bronze sculptures
- Roman Art. This is art from the Roman Empire and is characterized by sculptures, mosaics, and murals.
- Greek Art. This is art from ancient Greece. It spans eras such as the Geometric, Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic.
- Egyptian Art. This is art from ancient Egypt. It is characterized by pyramids, statues, and hieroglyphs.
#5. The Art Style and Period
You can group art based on the style, period, era, or movement under which it was made. Art produced in a specific period tends to share similar techniques, philosophy, and style that differentiate them from other periods.
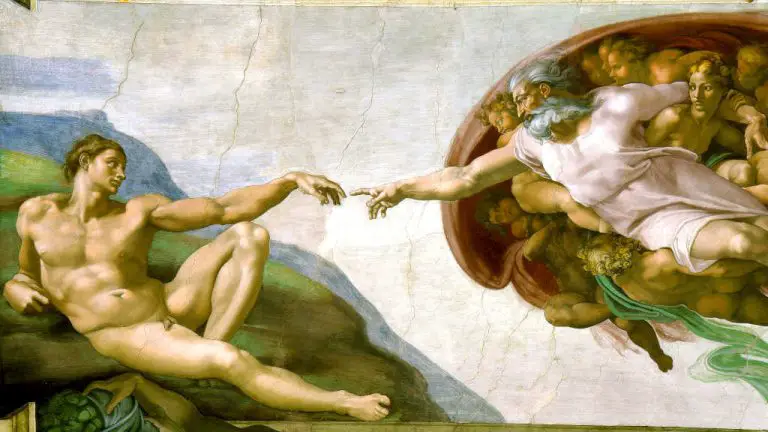

Here are types of art based on art periods. [3], [4], [5]
- Ancient Art. This covers art made before 400AD. It includes Prehistoric, Roman, Greek, Minoan, and Egyptian Art.
- Medieval Art. This covers art made between 400 and 1350 AD. It includes Early Christian, Gothic, Byzantine, and Romanesque Art.
- Renaissance Art. This covers art made between 1350 and 1600 AD. It includes Early, High, Northern, and Late Renaissance Art.
- Baroque Art. This covers art made between 1600 and 1750 AD. It includes Rococo (Late Baroque).
- Neoclassical Art. This covers art that was made between 1750 and 1800 AD.
- Romantic Art. This covers art made between 1800 and 1850 AD. It includes the Nazarene movement, Purismo, and Luminism.
- Modern Art. Art produced between 1850 and mid-1940sAD. It includes impressionism, cubism, art nouveau, and surrealism.
- Contemporary Art. This covers art produced from the mid-1940s to the Present. It includes Pop Art, Post Modern Art, Op Art, and Conceptual Art.
#6. The Function of the Art
Art plays numerous functions in society such as religious instruction, fostering cultural identity, and propagating political ideology.
You can use these functions to categorize art, for example:
- Religious Art: This includes art from major religions such as Islamic Art, Christian Art, Buddhist Art, and Hindu Art.
- Political Art: This includes propaganda literature, war posters, protest art, political cartoons, and satire.
- Commercial Art. This includes copywriting, product design, advertising art (video, pamphlets, posters, and billboards), packaging art, and branding art (web design).
- Therapeutic Arts. This includes journaling, coloring, and dancing.
5. Types of Art Explained (with Examples)
As we have discussed above, it is difficult to fit art into neat categories. No one method of classifying art will adequately meet all needs.
In this article, for the sake of simplicity, I will break down the examples of art into 4 major types. [2], [6], [7]
- Fine Arts (Visual Fine Arts)
- Applied Arts
- Literary Arts
- Performing Arts
The majority of art examples should be adequately covered by these 4 types of art.
#1. Fine Arts (Visual Fine Arts)
When we think of art, fine art is what often comes to mind. However, the definition of fine art can be a bit confusing.
What is Fine Art?
Fine art is any art that is created mainly for aesthetic appeal. This kind of art does not have utilitarian value and is meant primarily for enjoyment. [8], [9], [10]
Traditionally, fine art is broken down into three types: [10]
- Visual fine arts (which involves the creation of aesthetic art objects like paintings, drawings, and sculptures).
- Performing arts (which involves performance with no objects created).
- Literature arts (which involves written works).
However, the definition of fine arts has evolved in common use, and now primarily refers to visual fine arts, with performing and literary arts being separated into their own categories. [8], [10]
Characteristics of Visual Fine Arts
To simplify the classification process in this article, I use the latter definition, where I refer to fine arts as visual fine arts.
I discuss other aspects of fine art (such, as performing and literary arts) separately.
Visual fine arts have the following characteristics:
- They are created for appreciation through the sense of sight.
- They have no functional (utilitarian) value.
- They include 2D (such as paintings and drawings) or 3D still works (such as sculpture) and moving works (such as video, animations, and kinetic sculptures), but exclude performing and literary works.
Examples of Visual Fine Arts
Here are the common examples of visual fine arts.
- Painting. This is the art of making images or pictures using paints or pigments. It is commonly done on paper or canvas. Examples include watercolor, oil, spray, graffiti, and acrylic paintings.
- Drawing. This is the art of making pictures or images using materials like pencils, pens, charcoal, chalk, or crayons. Examples include pen, ink, chalk, crayon, and charcoal drawings.
- Sculpture. These are three-dimensional works of art made from materials like stone, metal, ceramics, and wood. Examples include relief, kinetic, 3D, models (clay, wax, soap), carvings (wood), and metal cast.
- Printmaking. This is the art of printing patterns, text, or images on paper, wood, metal, textiles, and other materials. Examples include woodcut, linocut, lithography, and screen printing.
- Photography. This is the art of capturing images using a camera. Photography can be done using film or digital media. Examples include portrait, wildlife, landscape, food, and fashion photography.
- Filmmaking. This is the art of making films or movies. Examples include movie making, home movies, journalistic filming, and sports filming.
- Animation. This is the art of making movies by manipulating images, drawings, or models to make them appear to move. Examples include stop motion, motion graphics, and 3D animation.
#2. Applied Arts
Applied arts have far-reaching impacts on our lives. You can see applied arts in kitchenware, advertisements, buildings, vehicles, appliances, and various tech gadgets.
What is applied art?
Applied art is a type of art that enhances the aesthetic appeal of functional objects. In applied art, we use various art techniques to beautify practical objects that we use every day. [11]
For example, an ornately carved door or table is a product of applied art.
Applied art can be categorized into two broad categories.[11]
- Decorative Arts. This mainly deals with techniques used to decorate functional objects.[12] Examples include printing, etching, and mosaic.
- Design. This deals with improving the aesthetics of objects but also their function. [13] Examples include fashion design, interior design, and interior design.
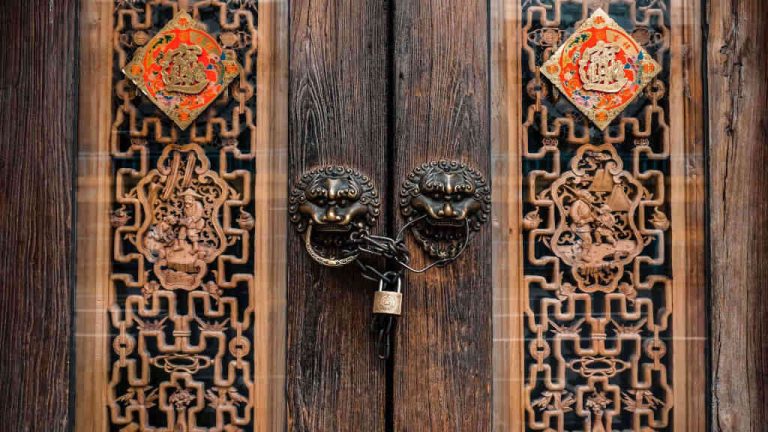

Characteristics of Applied Art
Here are some common characteristics of applied art.
- They beautify functional objects. Applied art techniques are used to decorate practical objects that we use every day.
- They are a type of visual art. Applied arts are appreciated through our visual senses i.e. they are aesthetically pleasing visually.
- They often have commercial intent. Applied art is used to decorate objects that are meant to be sold. In such cases, decoration increases the value of the object.
Examples of Applied Art
Here are examples of applied art broken down by type (i.e. Decorative and Design Arts).
Decorative Arts Explained (with Examples)
Decorative art is used to beautify functional objects like pots, glass, doors, tables, windows, or baskets. [12]
Some important characteristics of decorative arts
- They result in tangible objects. They often result in objects that you can touch such as baskets, mats, or pots.
- They improve the aesthetics of useful objects. This can result in intricate and beautifully decorated objects that are useful in everyday life.
- They have been practiced for centuries. There is evidence of decorated pottery dating back as far as 14,000 BCE.
Examples of decorative art include:
- Carving. This is the cutting of designs in materials like wood or stone. It is often used to decorate doors, windows, and furniture.
- Gilding. This is the application of a thin layer of gold on other surfaces. It is often used to decorate weapons, armor, or utensils.
- Needlework (such as embroidery, macramé, or quilting) is used to decorate wall hangings, blankets, mats, or clothes.
- Printing Techniques (such as screen, tie-and-dye, or stencil) are used to decorate textiles, leather, and fabric items.
- Enameling. Here, colored enamel is fused to metals using high heat. It is often used to decorate utensils like plates or cups.
- Mosaic. This is the use of small pieces of stone or glass to create patterns. It is often used to decorate walls or floors.
Design Explained (with Examples)
Design is concerned with conceptualizing and making products that are beautiful and functional. In design, improving function is as important as enhancing aesthetics. [13]
To quote Steve Jobs: “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
Some important characteristics of design are:
- Its outputs can be tangible objects (such as clothes in fashion design) or intangible (such as a website in web design).
- It aims to improve the aesthetics but also the function of the outputs. For example, when designing a user interface (UI) of a web page or app, the aim is to make it look appealing but also improve the navigation.
- It is relatively modern. Design incorporates many modern art forms that don’t fit under decorative arts.
- Incorporates other disciplines apart from art (such as engineering and science).
Examples of Design arts include:
- Industrial design. Here, design is used in mass-produced products like soda bottles, cars, or computers.
- Architectural design. Here, design is used to enhance the looks and functionality of buildings.
- Cartographic design. Here, design is used to create beautiful maps.
- Graphic design. Here, design is used to enhance created works in books, brochures, posters, or billboards.
- Interior design. Here, design is used to beautify the interior of buildings (such as houses, hotels, and offices).
- Fashion design. Here, design is used to make beautiful clothes.
#3. Literary Arts
Literary art is a powerful art form that has fostered political, cultural, and religious revolutions the world over.
Your views, ideas, and beliefs are likely influenced by something someone wrote down at some point in history.
What is Literary Art?
Literary art is art that is expressed in written form. The artist expresses ideas, beliefs, and emotions through the written word. [14]

Functions of Literary Art
Some of the functions of literary art include:
- Providing instruction on how to live life. This is done through religious, philosophical, and cultural works.
- Educating and informing. This is often done through non-fiction works such as self-help and journalism.
- Preserving information and ideas for posterity. This is done through non-fiction works such as historical texts, biographies, or folklore.
- Entertaining. This is commonly done through fiction, poetry, or drama.
Types of Literary Arts (with Examples)
Literary works fit into five main types. [15], [16]
- Non-fiction writing This is factual writing based on real people and events. Examples include biographies, letters, historical works, speeches, self-help, and philosophy.
- Fiction writing. This is writing based on made-up stories. Examples includefantasy, romance, mysteries, and graphic novels.
- Poetry. This is writing that is characterized by rhyme and rhythm. Examples include free verse, limericks, haiku, and sonnets.
- Drama. This is literature created to be performed in front of an audience. It often takes the form of a written dialog or script. It includes tragedies, comedies, melodramas, and musical dramas.
- Folklore. These are stories, customs, and beliefs of a particular culture that have been passed down orally over many generations. They include fables, fairy tales, legends, jokes, and proverbs.
#4. Performing Arts
This is a popular form of art that encompasses a variety of activities. It is not to be confused with the similarly named Performance Art (see the FAQ section).
What is Performing Art?
Performing art is a form of art that is meant to be performed live in front of an audience. [17]
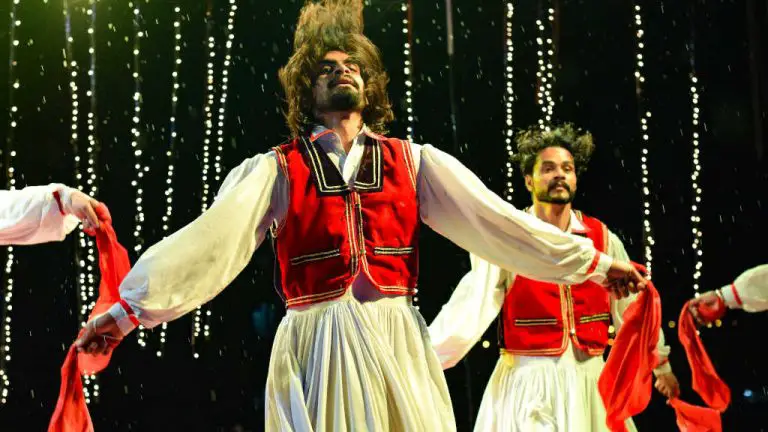

Here are some common characteristics of performing arts.
- Artists use their bodies as a way to express themselves.
- It results in an event rather than a tangible object or artifact.
- It is often temporary (unless recorded on video).
Functions of Performing Arts
Here are some popular functions of performing arts.
- Entertainment. This is the primary function of most performing arts.
- Preservation of tradition and culture. Cultural celebrations often involve music, dances, and plays.
- Religious observance. Religious rites incorporate music, dances, and other performances.
- Political and cultural protest. Performing arts have been used to drive political and social change.
Examples of Performing Arts
Performing arts are creative activities performed before an audience. These include:
- Music. This is an art form where sounds are used to create harmony, melody, and rhythm.
- Dance. This is an art form where the performer uses rhythmic body movements (usually timed to music) to express emotions or tell stories.
- Cinema. This is a form of art that uses moving pictures to tell a story.
- Theater. This is an art that involves the on-stage performance of a play. Drama, on the other hand, refers to the written play (which is a literary art).
- Mime and pantomime. These are forms of artwhere the performer tells a story through body movements (without words).
- Stand-up comedy. This is an art where the performer tells jokes and funny stories on stage.
- Magic. This is the art of producing illusions to entertain audiences.
- Circus. This is an art where performers use trained animals or exhibit extraordinary skills to entertain. Circus acts often include acrobatics, animal acts, and clowns.
Types of Art FAQs
Art terms and definitions can be confusing, and this can impact our ability to classify art. In this section, I will explain some of these confusing terms.
#1. What is the difference between art and fine art?
Art is a broad term that applies to many forms of creative expression. It encompasses all types of fine art (such as visual, performance, and literary art), but also applied art (functional art).
Fine art is a sub-category of art that is concerned mainly with aesthetics and self-expression and not function.
#2. What is the difference between fine art and visual art?
Fine art is art produced primarily for aesthetics and enjoyment and has no practical value. In the traditional definition, fine art is much broader than visual art because it encompasses visual forms of art (such as paintings and drawings), as well as performing and literary arts.
Visual art is art that is appreciated primarily through sight. Visual art results in beautiful works but unlike fine art, it encompasses works produced for aesthetics (such as fine art) and works that consider both aesthetics and function (such as applied art).
#3. What is the difference between applied art and fine art?
Applied art is often discussed in contrast to fine art and although both produce beautiful objects, they differ in the intention behind the creative process.
In fine art, the artist is mainly concerned with self-expression and producing aesthetically pleasing objects. Products of fine art don’t have a specific function and are made to be admired, provoke emotions, or for intellectual stimulation. Also, although such objects can be sold, making money is not a primary objective.
In applied art, the artist is mainly concerned with producing objects that are both beautiful and functional. Often, objects made through applied art are for sale. In applied art, the artist considers both the utilitarian and commercial potential of the artwork.
#4. What is the difference between applied art and crafts?
Applied arts, and specifically decorative arts, are art techniques used to decorate functional objects made through crafting.
With crafting, you can make purely functional objects (without any decorations). You can also make objects that are both functional and beautiful, using various art techniques.
For more on this, you can check out my article on the differences between arts and crafts.
#5. What is the difference between performing arts and performance arts?
Performing art is a form of art that is performed before a live audience. Examples of performing arts include dancing, theater, and circus acts. [17]
Performance art is an unconventional form of art that features a live presentation that incorporates aspects of dance, acting, music, and painting. It aims to communicate political or cultural ideas, often through shocking or provocative means. It has been particularly popular with feminists and war protesters. Examples of performance art include body art, happenings, and action painting. [18], [19]
Wrapping Up
In this article, my aim was to give you a general overview of the various ways you can classify art and the challenges involved.
Hopefully, you have found a framework that you can use to fit in any artwork you encounter.
If you are an artist or wish to be an artist, you should now have a better idea of where your art fits. This will help you as you explain your art to others.
This article is part of a series that explores arts and crafts. You can check out the other articles in the series below.
